The aviation sector is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by increasing globalization, rising passenger numbers, and advancements in technology. India, in particular, is poised to become the third-largest aviation market globally by 2030, with consistent expansion in domestic and international routes. This surge has created a demand for skilled professionals across various domains, making aviation a promising career choice.
Our Presence Across The World

INDIA

UK

USA

UAE
Opening Shortly
Why Choose Sha-Shib?
If you want to excel in your aviation career, it is crucial to choose the best aviation institute to study your dream aviation course. Sha-Shib Group of Institutions, in fact, stands as the best AME and aviation training institute in South Asia.
Airport Presence
Functional Aircrafts
Flying Aircraft for Training
Practical Tie-Ups
AME Colleges in India
MRO Bases & Sub-bases
Aircraft at Our Campus

Maximum Speed
140 mph
Wing Loading
14.1 lb/sq ft
Power
160 BHP at 2400 rpm

Maximum Speed
158 mph
Wing Loading
18.6 lb/sq ft
Power
8.9 lb/hp
Scholarships upto 4 crores will be distributed among the eligibles
Apply for Scholarship cum Entrance Exam (SSAT-2025)

Group's Own Aircraft Maintenance Repair Overhaul Organizations
Approved by DGCA, Govt. of India
International Aircraft Sales Pvt. Ltd. (MRO) Bhopal
Indian Aerospace & Engineering (MRO) Navi Mumbai
Aerospace Research & Development Centre (MRO) Guwahati
Aerospace Research & Development Centre (MRO) Jamshedpur
Hindustan Aerospace & Engineering (MRO) Karad, Maharashtra
Hindustan Aerospace & Engineering (MRO) Pune
International Aircraft Sales Pvt. Ltd. (MRO) Noida
Aerospace Research & Development Centre (MRO) Bhubaneshwar
International Aircraft Sales Pvt. Ltd. (MRO) Mandsaur
Aerospace Research & Development Centre (MRO) Pune
Sha-Shib Flying Academy (MRO) Guna
Air 7 Star Ratlam
Air Allegiance Chhindwara
Our Gallery
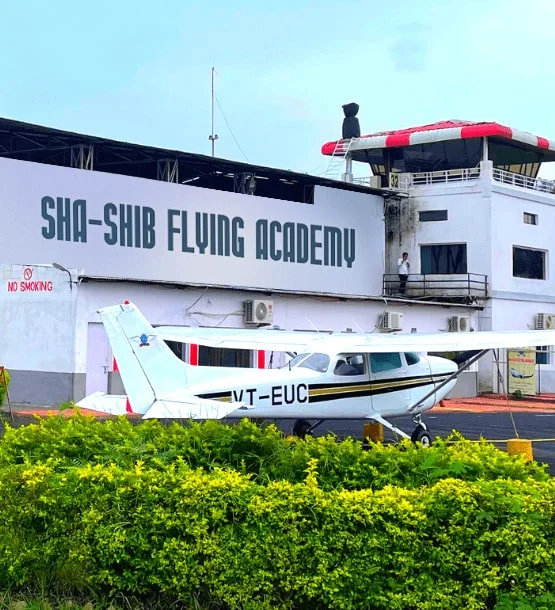

Life At Sha-Shib Flying Academy
At SFA, we consider flight training to be more than simply getting a licence; it's also about learning the skills and information needed to become a capable and safe pilot. We are proud of our cutting-edge facilities, knowledgeable professors, and extensive training programmes that are tailored to the requirements of prospective pilots. SFA recognises that flight training may be an expensive commitment and works to provide our students with training alternatives that are within their budgets. If you want to pursue a profession in aviation our training programmes are tailored to fulfil the demands of a wide range of pupils.
Major Recruiters
These organizations providing jobs after completion of our course.
Admission 2025 Open Now
Submit your details to get a call back
Feedback from our students
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Significance of an Aircraft Maintenance Engineering Course (AME)?
Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of aviation operations. The aviation sector is one of the most regulated industries globally, with stringent guidelines set by authorities to guarantee the airworthiness of aircraft. In India, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) oversees all aspects of civil aviation, including the certification and licensing of Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs). An AME course equips individuals with the technical expertise and practical skills required to maintain, repair, and inspect aircraft. The curriculum covers various aspects of engineering, focusing on aerodynamics, avionics, propulsion systems, and the operational safety of aircraft. The comprehensive nature of this course ensures that candidates are well-prepared to meet the challenges of the aviation industry.
To work as an AME in India, individuals must complete a DGCA-approved training program and fulfill the practical experience requirements. Following the training, candidates must pass the DGCA's licensing test to receive the AME license. This license is a mandatory certification that authorizes engineers to work in the aviation sector, particularly in Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) organizations. The Indian Aircraft Act of 1934 provides the legal framework for regulating aviation in India, including the licensing and certification of AMEs. Compliance with this act ensures that the highest safety standards are maintained across the aviation sector. Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs) are entrusted with the responsibility of ensuring that every aircraft adheres to these standards before takeoff.
The AME course also opens doors to diverse career opportunities in the aviation industry. Graduates can work in airlines, MRO organizations, and even manufacturing units, where engineering expertise is crucial. The demand for qualified AMEs is growing rapidly, driven by the expansion of global and domestic air travel. In conclusion, an AME course is more than just a training program; it is a pathway to a rewarding career in aviation. By obtaining a DGCA-certified license, engineers demonstrate their competence in maintaining and repairing aircraft in line with legal and industry standards. With the increasing reliance on advanced engineering technologies in aviation, the significance of the AME profession continues to rise, making it an essential component of the aviation industry's success.
What is the difference between Private Pilot Licensing and Commercial Pilot Licensing
Aviation offers numerous paths for aspiring pilots, with private pilot licensing (PPL) and commercial pilot licensing (CPL) being two essential certifications. While both licenses enable individuals to operate airplanes, their purpose, requirements, and career opportunities differ significantly. A private pilot license (PPL) is designed for individuals who wish to fly airplanes for personal or recreational use. With a PPL, pilots can engage in non-commercial activities, such as leisure flying, personal transportation, or exploring aviation as a hobby. To obtain a PPL, candidates must complete a training program at approved institutions, meet specific medical standards, pass a written knowledge exam, and successfully complete a practical flight test. While PPL medical requirements are less stringent than those for a CPL, physical fitness is essential to ensure safety in the skies. Pilots with a PPL are not authorized to operate airplanes for remuneration or engage in commercial activities.
In contrast, a commercial pilot license (CPL) allows individuals to operate airplanes for compensation. CPL holders can pursue professional aviation careers, including roles with airlines, charter services, or cargo operations. In India, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) regulates pilot licensing, ensuring compliance with global aviation standards. To obtain a CPL, pilots must log at least 200 hours of flight time, which includes 100 hours as Pilot-in-Command (PIC) and 20 hours of cross-country flying. CPL training at DGCA-approved institutions is more rigorous, focusing on advanced aviation techniques, navigation, and safety protocols. CPL holders are often required to gain practical experience in Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) settings, which provides them with an understanding of airplane systems and maintenance procedures. The CPL demands higher medical fitness standards and advanced technical skills due to the responsibilities associated with commercial aviation.
The primary distinction between a PPL and a CPL lies in their intended use. While a PPL is tailored for recreational flying, a CPL opens doors to a professional aviation career. The training for a CPL is more comprehensive, requiring a significant commitment to mastering advanced flying skills and adhering to stringent regulations set by the DGCA. In conclusion, choosing between a PPL and a CPL depends on an individual’s goals in aviation. Both licenses offer unique opportunities, but a CPL is essential for those aspiring to work in commercial aviation and operate airplanes professionally.
Difference Between AME, Aeronautical Engineering, and Aerospace Engineering
Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) focuses on maintaining, repairing, and ensuring the airworthiness of aircraft. AMEs are licensed professionals responsible for inspecting, troubleshooting, and certifying aircraft before flight. In India, AMEs must undergo a DGCA-approved training program, fulfill practical experience requirements, and pass licensing exams. AME is not a conventional degree program but rather a specialized certification that equips individuals to work in Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) organizations or airlines.
Aeronautical Engineering deals with the design, development, and manufacturing of aircraft within Earth's atmosphere. It encompasses studying aerodynamics, propulsion systems, and avionics to improve aircraft performance. Aeronautical engineers typically work on designing commercial planes, military jets, helicopters, or drones. This field requires a degree in engineering, such as a Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech) or Bachelor of Engineering (B.E.), and offers career opportunities in research organizations, manufacturing companies, or aviation firms.
Aerospace Engineering is broader and includes both aeronautical and astronautical engineering. While aeronautical engineering focuses on atmospheric flight, astronautical engineering involves the study and development of spacecraft that operate beyond Earth’s atmosphere. Aerospace engineers work on advanced technologies like satellites, rockets, space stations, and interplanetary missions. This field demands expertise in thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and advanced propulsion systems, and typically requires a degree in engineering. In summary, AME is a practical certification aimed at maintaining and certifying aircraft for safe operation, aeronautical engineering specializes in aircraft design and development, and aerospace engineering spans both atmospheric and space-related vehicle design. Each discipline offers unique career opportunities based on interests and aspirations within the aviation and space industries.
What is the role of DGCA in regulating AME institutions and the Aviation sector?
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the aviation industry in India. It plays a vital role in regulating Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) and pilot training institutions across the country. The DGCA grants approval to AME institutions, enabling them to train students in the maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) of aircraft. This approval signifies that an institution meets the necessary standards in infrastructure, facilities, and faculty to deliver high-quality training. It also ensures that the curriculum aligns with the regulations and guidelines established by the DGCA. By maintaining strict oversight, the DGCA ensures that these institutions adhere to the safety and technical standards required in the aviation sector. DGCA approval is essential for AME institutions, as it reflects their compliance with the regulatory authority's benchmarks. This not only builds trust among students and industry stakeholders but also enhances the quality of aviation training in India.
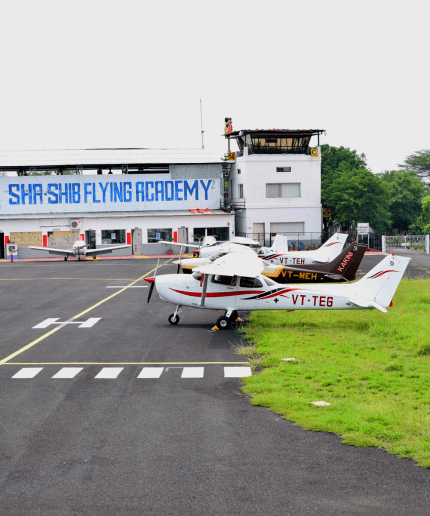

Sha-Shib Flying Academy: Reshaping the Flying Experience with Modern Technologies
Sha-Shib Flying Academy (SFA), a premier aviation training institution under the Sha-Shib Group of Institutions, is setting new benchmarks in pilot education in India. As a single-point destination for aspiring and current pilots, SFA offers a comprehensive training program that combines ground-level learning with advanced in-flight training, enabling students to transform their aviation dreams into reality. At Sha-Shib Flying Academy, pilot training is meticulously structured to guide students from foundational concepts to acquiring their licenses. The training program is divided into various stages but is designed as a unified course to provide an immersive learning experience. Students can begin flying as soon as they complete their ground school training, ensuring a seamless transition from theoretical knowledge to practical application. SFA’s curriculum is aligned with the standards set by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), India’s aviation regulatory authority. This alignment ensures that students are not only well-prepared to earn their pilot licenses but are also equipped with the skills and knowledge required to meet industry demands.
State-of-the-art facilities and Modern Technologies
Sha-Shib Flying Academy stands out by offering training on state-of-the-art aircraft equipped with the latest technologies. Hands-on experience with advanced systems is crucial for developing the skills necessary to operate modern aircraft/airplanes effectively. These cutting-edge facilities provide students with an edge in a competitive industry, ensuring they are ready to tackle complex flight operations and adapt to evolving aviation technologies. The academy’s investment in innovative tools and technologies reflects its commitment to delivering world-class education. By training on modern aircraft, students gain confidence and competence, which are essential traits for a successful aviation career.

Expert Faculty and Personalized Guidance
At SFA, students benefit from the expertise of experienced instructors who bring extensive industry knowledge to the classroom and cockpit. These instructors provide personalized guidance, helping students master both technical and soft skills. The faculty's commitment to excellence ensures that every trainee receives the support needed to excel in their journey to becoming a professional pilot.

Meeting the Growing Demand for Skilled Pilots
The global aviation industry is witnessing unprecedented growth, with air travel becoming increasingly accessible and airlines expanding their fleets to meet passenger demand. This trend is particularly evident in India, with the country poised to become one of the largest global aviation markets. This growth has created a surge in demand for well-trained pilots capable of managing complex situations and ensuring passenger safety.
Sha-Shib Flying Academy recognizes this industry need and positions itself as a leader in shaping the next generation of aviators. Through rigorous training and adherence to global standards, the academy prepares students to meet the challenges of the modern aviation landscape.

Unlocking Lucrative Career Opportunities
A career as a pilot is not only highly respected but also offers exceptional earning potential and opportunities for international travel. The aviation industry provides a dynamic work environment where professionals can explore the world while enjoying the prestige associated with the profession. By enrolling in Sha-Shib Flying Academy, students gain access to a wide array of career opportunities in both commercial and private aviation sectors. The academy’s comprehensive training equips them with the skills to secure positions with leading airlines or embark on specialized aviation paths, such as corporate piloting or charter services.

Sha-Shib Flying Academy: The Pathway to Success
Sha-Shib Flying Academy’s mission is to empower aspiring pilots with the tools and resources needed to achieve their dreams. As part of the renowned Sha-Shib Group, the academy is recognized as a leading aviation training institute and a premier pilot academy in India. With a curriculum that emphasizes safety, efficiency, and technical expertise, SFA lays a solid foundation for students to build successful aviation careers.
Renowned as a top-tier flight academy in India, Sha-Shib Flying Academy combines state-of-the-art facilities, experienced instructors, and innovative teaching methods to provide a clear and structured pathway for students to excel in the aviation industry. Graduates of SFA are not only skilled pilots but also confident professionals poised to make their mark in the skies. SFA is redefining aviation education in India by blending advanced technologies with a comprehensive training approach. From ground school to advanced flight training, the academy delivers a holistic learning experience that prepares students for thriving careers in aviation. As the best pilot training in India, SFA offers an unparalleled opportunity for individuals with dreams of flying to turn their ambitions into reality.
Through rigorous training, expert mentorship, and cutting-edge facilities, Sha-Shib Flying Academy is shaping the future of the aviation industry. The academy’s pilot course in India is meticulously designed to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and confidence needed to excel. SFA also offers specialized aircraft maintenance engineering (AME) courses to meet the growing demand for skilled aviation professionals. These programs provide hands-on experience and ensure students are industry-ready and capable of excelling in their aviation careers. By integrating AME training with advanced pilot courses, Sha-Shib Flying Academy stands as a beacon of excellence in aviation education. Aspiring pilots and AME students benefit from unmatched resources and guidance, making SFA the ideal aviation training institute for pursuing a career in the skies. With a commitment to innovation, education, and professional development, Sha-Shib Flying Academy ensures every trainee emerges as a skilled and confident aviation professional ready to tackle the challenges of the modern aviation industry.

Why Choose Sha-Shib Flying Academy (SFA)?
Sha-Shib Flying Academy (SFA) in Guna, Madhya Pradesh, stands as a premier institute in aviation education, offering a blend of cutting-edge training and real-world experience. Backed by the Sha-Shib Group, the largest group in South Asia for Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) training, SFA provides unmatched opportunities for aspiring aviation professionals, and it is the best flight academy in India. Under the Sha-Shib Group, nine aircraft maintenance engineering (AME) colleges are running.
Practical Training Facilities
SFA offers a state-of-the-art infrastructure that enhances the learning experience for students. Its own Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) facility at the Guna Airport, approved by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) under CAR 145 for base and line maintenance, ensure hands-on exposure to actual aircraft/airplanes maintenance processes. Additionally, SFA operates a DGCA-approved Continuous Airworthiness Management Organisation (CAMO), where students gain expertise in maintaining airworthiness standards. This crucial aspect of aviation safety equips students with the skills necessary to manage and ensure safe aircraft or airplanes flying. The campus also features a functional aircraft hangar and live aircraft from customers who come for maintenance at the MRO. Practical tie-ups with organizations like AI Engineering Services Ltd (AIESL) provide further exposure to real-world scenarios, ensuring students are industry-ready upon graduation.
Advanced Learning Resources
SFA's commitment to excellence is reflected in its well-equipped labs and workshops. These include instrument labs, electrical labs, radio navigation labs, jet and piston engine labs, airframe shops, and machine shops. The technical library further supports students’ theoretical understanding, complementing their practical training.
DGCA-Regulated and International Standards
All training at SFA is regulated by DGCA, Government of India, and adheres to international standards, and SFA is the best flight school in India under Sha-Shib Group of Institutions approved by DGCA, Government of India. This ensures that students receive world-class education and are prepared for global aviation industry demands. Sha-Shib Flying Academy offers aviation pilot training courses.
SFA provides specialized Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) courses in:
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineering Mechanical (AME) B1.1
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineering Mechanical (AME) B1.2
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineering Avionics (AME) B2
The academy also offers additional graduation programs like AME + BSc/BBA, allowing students to earn dual qualifications and broaden their career prospects. Sha-Shib Flying Academy combines theoretical rigor with practical expertise, offering unparalleled training facilities and industry exposure. With its commitment to excellence and strong backing from the Sha-Shib Group, SFA is the ideal choice for aspiring aviation professionals who aim to build a successful career in the skies.
Courses Provided by Sha-Shib Flying Academy
Aircraft Maintenance Engineering
Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) is a specialized program designed to prepare individuals for a career in maintaining and ensuring the airworthiness of aircraft. This field plays a critical role in the aviation industry, as safety and efficiency rely heavily on well-maintained aircraft. The Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) course is tailored to provide a blend of theoretical knowledge and hands-on training in aircraft systems, avionics, and propulsion. Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) is differed from another engineering courses, it is a licensed program. The curriculum typically includes subjects such as aerodynamics, electronics, materials science, and regulations. Students gain proficiency in diagnosing and repairing complex aircraft systems, conducting routine maintenance, and adhering to stringent safety standards. Advanced modules may cover specific aircraft models, engines, or avionics systems, offering a pathway to specialized certifications.
Sha-Shib Flying Academy offers comprehensive Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) courses tailored to meet industry standards. These courses cover critical aspects of aircraft maintenance, ensuring students acquire the technical skills required to inspect, repair, and maintain aircraft. The AME curriculum includes specialized training in Mechanical B1.1, Mechanical B1.2, and Avionics B2 categories. With access to a state-of-the-art MRO facility and DGCA-approved programs, students at SFA are industry-ready upon completing their AME education. The institute provides opportunities to enhance practical skills with real-world exposure to engineering processes. Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) plays a critical role in the aviation sector by ensuring the safety, airworthiness, and operational efficiency of aircraft. Licensed Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs) are responsible for certifying aircraft, aeroplanes, and their components before they are released for service, adhering to regulations set by authorities like the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This prestigious profession demands precision, responsibility, and adherence to stringent global aviation standards.
Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs) oversee and certify tasks such as major repairs, overhauls, and regular maintenance of aircraft, power plants, and their systems. Their work ensures compliance with both domestic and international aviation safety standards. AMEs find employment with airlines, maintenance and repair organizations (MROs), flying clubs, and aerospace companies, where they play an indispensable role in certifying aircraft for safe operation under government regulations. To become a certified AME, aspiring professionals must complete an Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) course at a DGCA-approved institute. These programs offer a comprehensive curriculum, combining theoretical knowledge and practical training to meet the highest standards of aviation safety. As the global aviation industry expands, the demand for skilled AMEs continues to grow, making Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) a promising and rewarding career path with abundant opportunities.


Pilot Training
Aspiring pilots can pursue their dreams through the professional pilot training courses offered by SFA. These courses include training for Private Pilot License (PPL) and Commercial Pilot License (CPL). The curriculum focuses on core areas such as aircraft operations, flight controls, navigation, meteorology, and aviation safety. SFA’s training programs are conducted under DGCA regulations, ensuring students receive a high-quality education. The advanced simulators and real-world flight training sessions prepare students to excel in the competitive aviation industry. SFA is regarded as the best aviation academy in India approved by the DGCA government of India.


Why Choose Aviation as a Career ?
The aviation industry is more than just planes and airports—it is the lifeline of global connectivity, enabling trade, travel, and cultural exchange. It offers exciting career opportunities that blend technical expertise, leadership, and interpersonal skills. For those passionate about innovation, teamwork, and exploring new horizons, aviation presents a dynamic and rewarding career path.
A Growing Industry with Endless Opportunities
High Demand for Skilled Professionals
The global aviation industry consistently demands professionals in diverse roles, including pilots, aircraft maintenance engineers (AMEs), aviation managers, air traffic controllers, and cabin crew. India’s aviation sector alone requires thousands of trained individuals annually to meet the needs of its expanding airline fleets, new airports, and increasing passenger traffic. In addition to passenger services, the growth of cargo operations, drone technologies, and private jet charters has further diversified the career opportunities in aviation. This demand ensures job security and career growth for individuals pursuing aviation education and training.
Future Growth of the Aviation Industry in India
India’s aviation industry is fuelled by :
Rising Middle-Class Population:
With a growing middle class, air travel is no longer a luxury but an accessible mode of transportation.
Investment in Infrastructure:
Modernization and expansion of airports are creating additional jobs for aviation professionals.
Government Initiatives:
Programs like UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) aim to enhance regional connectivity, leading to the development of smaller airports and an increased need for trained personnel.
Technological Advancements:
The adoption of smart technologies in airport management and air traffic control systems requires a skilled workforce to operate and maintain these systems.
India’s ambitious plans to double its passenger traffic over the next decade highlight the critical need for aviation education and specialized training to meet industry demands.
The Importance of Aviation Education
Aviation education is the cornerstone of a successful career in the industry. It provides students with the technical skills, practical training, and industry knowledge needed to thrive in various roles.
Holistic Understanding of the Industry
Aviation education covers a broad spectrum of topics, including:
- Flight Operations: Understanding the mechanics of flight, navigation, and safety protocols.
- Aircraft Maintenance: Ensuring airworthiness through routine checks and system upgrades.
- Air Traffic Management: Coordinating flights to ensure efficient and safe airspace use.
- Aviation Safety and Compliance: Adhering to international regulations and ensuring passenger safety.
Courses like BBA in Aviation Management, Pilot Training, Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) , and Cabin Crew Training equip students with specialized knowledge and practical experience to excel in their chosen fields.
Opportunities in India and Abroad
Aviation courses in India are globally recognized, providing students with opportunities for international careers. Indian training programs boast world-class facilities, experienced instructors, and strong industry collaborations. Certifications such as International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) compliance enhance global employability for students aspiring to work abroad. Aviation education opens doors to diverse career paths, including roles such as pilots, who ensure safe and efficient flights while exploring the world; aircraft maintenance engineers (AMEs), critical to the safety and reliability of aircraft; air traffic controllers, who manage airspace and flight operations; cabin crew, dedicated to passenger comfort and safety; and aviation managers, who oversee operations and bring together technical and managerial expertise. The industry’s breadth ensures opportunities for individuals with varying interests and skills. The aviation sector operates on a global scale, offering professionals exposure to diverse environments and extensive travel opportunities. It promises job security, steady growth, and dynamic work environments powered by cutting-edge technology and teamwork. Aviation careers are also financially rewarding, with competitive salaries reflecting professionals' critical roles. Beyond personal benefits, aviation professionals contribute significantly to society by connecting people, facilitating global trade, and supporting humanitarian efforts, making it a career path with both personal and societal impact.
Key Areas of Aviation Education and Its Importance in India
The aviation industry is a cornerstone of global connectivity, commerce, and innovation. Its steady growth creates a need for a highly skilled workforce trained in various specialized areas. Aviation education offers a pathway for individuals to enter this dynamic field, equipping them with the skills and knowledge to excel. From pilot training to aircraft maintenance and beyond, aviation education is diverse, offering numerous career opportunities. This article explores key areas of aviation education, its importance in India, and the wide array of courses available, including aeronautical engineering, air hostess, and cabin crew training.
Pilot Training
Pilots are the backbone of the aviation industry, responsible for the safe and efficient operation of flights. Aviation education for pilots encompasses ground and flight training, covering critical topics such as:
- Aircraft Operations: Gaining knowledge about the mechanics and dynamics of flight.
- Flight Controls: Mastery of cockpit controls and their impact on aircraft performance.
- Navigation: Knowledge of air routes, charts, and modern navigation tools.
- Meteorology: Awareness of weather conditions and their influence on flight safety.
- Aviation Safety: Adherence to safety protocols and emergency procedures.

The journey to becoming a pilot is rigorous. Private training is categorized into two different categories, Private Pilot License (PPL) and Commercial Pilot License training (CPL). Aspiring pilots must complete foundational training at flying schools, pass written examinations, and log extensive flying hours to earn their commercial pilot licenses (CPL). Pilots are also trained to handle advanced technologies and diverse flight conditions. A student who completed their 10+2 with Physics and Mathematics can join a pilot course in India. Under the Sha-Shib Group of institutions, Sha-Shib Flying Academy provides the best pilot training in India. As the global aviation industry expands, the demand for highly skilled pilots continues to grow. India, as one of the fastest-growing aviation markets, is experiencing an unprecedented need for qualified pilots, driven by an increase in domestic and international air travel.
Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME)

Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (AME) is essential for maintaining the safety and dependability of air travel. Engineers in this field are tasked with inspecting, maintaining, and repairing aircraft to meet stringent regulatory standards. Students with a 10+2 qualification in Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics or a 3-year engineering diploma in Electrical, Electronics, Mechanical, and Aeronautical disciplines can join AME courses. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting routine maintenance checks.
- Troubleshooting technical issues.
- Upgrading aircraft systems.
- Ensuring compliance with airworthiness standards.
AMEs work with advanced technologies, including avionics and modern aircraft systems, to ensure safety and performance. With aviation technology constantly evolving, the demand for skilled maintenance engineers is on the rise. India’s growing fleet of aircraft and the advent of new models create numerous opportunities for professionals in this domain.
Aeronautical Engineering
Aeronautical engineering is a specialized field focusing on the design, development, and maintenance of aircraft and aerospace systems. This discipline integrates principles of mechanical engineering, electronics, and material science. Key areas of study include:
- Aerodynamics: The study of air movement and its impact on aircraft design.
- Propulsion Systems: Development of engines and power systems.
- Aircraft Structures: Designing lightweight yet strong components.
- Avionics: Advanced electronics used for navigation and communication.

Aeronautical engineers contribute to innovation in aviation by designing energy-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft. India's focus on self-reliance and the expansion of the aerospace industry has created a surge in opportunities within the field of aeronautical engineering.
Air Hostess and Cabin Crew Training

The cabin crew serves as the face of the airline industry, ensuring passenger comfort, safety, and service. Training programs for air hostesses and cabin crew focus on a mix of technical and interpersonal skills, including:
- Safety Procedures: Emergency response, first aid, and evacuation protocols.
- Customer Service: Managing diverse passenger needs with professionalism.
- Communication Skills: Effective interaction with passengers and crew.
- Personal Grooming: Adhering to the standards of appearance required by airlines.
The role of the cabin crew is not just limited to service; they are crucial in managing in-flight emergencies and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. With the boom in aviation and tourism, cabin crew professionals are in high demand across India and the world.
Aviation Management
Aviation management integrates technical expertise with business skills, equipping individuals for leadership positions within the industry. Topics covered include airline operations, airport management, and aviation law. Professionals in this field ensure the smooth functioning of aviation businesses.

Importance of Aviation Education in India
India's aviation sector has experienced exponential growth, fueled by a burgeoning middle class, government initiatives, and increasing connectivity between cities. The country’s emphasis on becoming a global aviation hub underscores the importance of aviation education.
Meeting the Demand for Skilled Professionals
India’s aviation market is projected to become the third-largest globally, necessitating a large pool of skilled professionals across various roles, including pilots, engineers, and cabin crew. Aviation education bridges this gap by producing industry-ready talent.
Boosting Economic Growth
The aviation industry contributes significantly to India's GDP. Well-trained professionals ensure operational efficiency, safety, and customer satisfaction, which are critical for the industry’s growth and its ripple effect on tourism, trade, and infrastructure development.
Enhancing Global Competitiveness
Quality aviation education enhances India’s competitiveness on the global stage. Indian professionals are recognized for their skills and expertise, with many finding opportunities abroad, strengthening the country’s reputation in the global aviation market.
Supporting Government Initiatives
Programs like UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) aim to make air travel accessible to smaller cities and towns. This initiative increases the demand for trained professionals to manage operations at regional airports and on newly introduced routes.
Encouraging Research and Innovation
Aviation education fosters a culture of research and innovation, essential for developing indigenous technologies and addressing challenges like sustainability and energy efficiency.
Aviation education is a gateway to a thriving career in one of the most dynamic industries. From pilot training and aircraft maintenance to aeronautical engineering and cabin crew training, the scope of opportunities is vast. In India, the importance of aviation education is underscored by the sector's rapid growth, its impact on the economy, and its role in connecting communities. By investing in comprehensive aviation education programs, India can meet the demands of its expanding aviation market and establish itself as a global leader in this field.